|
Physics
- 1997 ( I.C.S.E)
You are on Answer-1
Q 1(a)(i)How fast should a man weighing 60 Kg
run so that his Kinetic energy is 750 J?
(ii) A body of mass 1 Kg is thrown vertically up with an initial speed of
5 m/s. What is the magnitude and direction of force due to gravity acting
on the body when it is at its highest point?
Q 1 (b)Diagram given below shows a
weightless lever in equilibrium. Neglect friction at the fulcrum F.
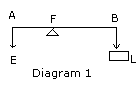
(i) State the principle of moments as applied to the above lever.
(ii) Define mechanical advantage and calculate its value for the given
lever.
(iii) Name the type of lever which has mechanical advantage greater than
1.
Q 1 (c) A body weighs 20 gf in air, 18.2 gf
in a liquid and 18.0 gf in water.
Calculate:
(i) The relative density of the body , and
(ii) The relative density of the liquid.
Q 1 (d) (i) Define 'Specific latent heat of
fusion of ice'. Give its S.I unit.
(ii) What is the effect of increase in pressure on the melting point of
ice and boiling point of water ?
Q 1 (e)Diagram 2 below shows a right angled
prism of refractive index 1.5. An object PQ is placed in front of its base
BC.
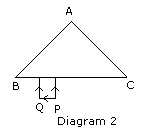
Copy the diagram.
(i)Complete the diagram showing the image produced by the prism.
(ii)Name an instrument in which such prism is used.
Q 1 (f)Diagram 3 below shows an object AB
placed on the principal axis of a convex lens placed in air. F1
and F2 are two foci of the lens.

Copy the diagram.
(i) Draw a ray of light starting from B and passing through O. Show the
same ray after refraction by the lens.
(ii) Draw another ray from B which passes through F2 after
refraction by the lens.
(iii) Locate the final image formed .
(iv) Is the image real or virtual ?
Q 1 (g) In the nuclear reaction given
below, a nucleus X changes to another nucleus Y.
88X226 --- Y - + energy.
(i) What are the atomic and mass numbers of Y ?
(ii) Name the gas formed when the - particles acquires two electrons.
(iii) What is the effect on the motion of the - particle when it passes
through a region containing a magnetic field ?
Q 1 (h) Diagram 4 below shows a circuit
containing a coil wound on a long and thin hollow cardboard tube.
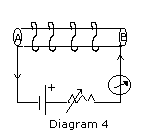
Copy the diagram.
i) Show the polarity acquired by each face of the solenoid.
ii) Draw the magnetic lines of force inside the coil and also show their
directions.
iii) Mention two methods to increase the strength of the magnetic field
inside the coil.
Q 1 (i)Ultra-violet light falls on a dry
zinc plate.
i) Name the particles emitted from the plate.
ii)What is the nature of charge acquired by the plate ?
iii) Name the phenomenon that takes place.
iv) Name one of the devices based upon the above phenomenon.
Q 1 (j)(i) Give one example each of the
materials suitable for making
1. Fuse wire and
2. Heater element
(ii) Define angle of dip. At what places on earth will the angle of dip be
1. Maximum and
2. Minimum
|
|
Ans.1n(a)(i)Let the velocity of man = v
m/s
Therefore his K.E = (1/2)(mv2) = 750 J
(given)
But m= 60 Kg Therefore (1/2)(60)(v2) =
750 J
Therefore v2 = 25 and v = 5
m/s
(ii)At the highest point the velocity = 0 and the mass
is attracted towards the earth due to gravity.
Therefore the magnitude of the gravitational force = F = mg
= 9.8 N downwards.
Ans.1 (b)(i) The principle of moments
states that the vector sum of the moments of all coplanar forces acting on
a body in the equilibrium state is always zero. In the given case of the
lever Anticlockwise moment of effort E about fulcrum F =
Clockwise moment of load L about fulcrum F
i.e E x AF = L x BF.
(ii)Mechanical advantage of a machine is defined as the ratio of the load
lifted L to the effort applied E.
i.e M.A = L / E = AF / BF
(iii)We know that M.A of a lever M.A = L /E = AF /BF
If M.A 1
Therefore AF (Effort Arm )/BF (Load Arm) 1
Hence, Effort Arm should be greater than Load Arm for a lever whose M.A is
greater than 1
Ans.1 (c)Weight of body in air = 20 gmf
Weight of body in liquid = 18.2 gmf
Weight of body in water = 18 gmf
Therefore loss in weight of body in liquid = 20 - 18.2 = 1.8 gmf
loss in weight of body in water = 20 - 18 = 2 gmf
R.D of body (solid) = weight of solid in air / weight of solid in water =
20/ 2 = 10
R.D of body(liquid) = loss in weight of solid in liquid / loss in weight
of solid in water = 1.8 / 2 = 0.9
Ans.1 (d)(i)The specific latent heat of
fusion of ice, is defined as the quantity of heat energy required to melt
a unit mass of ice at 0oC into the unit mass of water at 0oC.
Its S.I unit is Joules/Kg
Value = 336000 J/Kg
(ii)If the pressure is increased the melting point of ice decreases.
If the pressure is increased , the boiling point of water increases.
Ans.1 (e)(i)

(ii)Such a prism is used in prism binoculars.
Ans.1 (f)(i)
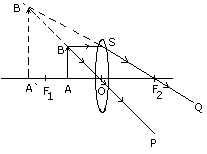
BO is incident ray starting from B and passing through O the emergent ray
is OP so that BP is a straight line . This ray passing through the optical
centre O, does not deviate.
(ii) Another ray BS which is parallel to the principle axis and passes
through the focus F2 after refraction by the lens. SQ is the
emergent ray through F2.
(iii) Producing PB and QS towards B1 which is the point image
of B and A1B1 is the final image formed.
(iv) The final image is virtual ,erect and magnified.
Ans.1 (g)(i) 88X226
« Y + + energy
88X226 « 86Y222 + 2He4
+ energy
Therefore, Atomic no. of 86Y222 = 86
and mass no. of 86Y222 = 222
(ii) We know that particle = He++ helium nucleus. On acquiring
2 electrons, the gas is formed
(iii) We know that a particle is positively charged particle. When
it passes through a region containing a magnetic field, it is deflected
strongly by the magnetic field and so it deviates from its original path.
Ans.1 (h)(i)

A is the North Pole and B is the South Pole
 |
(ii)
Magnetic field of induction inside the solenoid is almost
uniform. |
(iii)Magnetic field of induction inside the solenoid is given by B
= m o nI where, m o is the absolute
permeability of the free space , n is the number of turns per unit length
of the solenoid and I is the current passing through the solenoid.
Therefore, magnetic field inside the coil can be increased by the
following two methods :-
1. By increasing the current in the coil.
2.By increasing the number of turns per unit length.
Ans.1 (i) i) When Ultra-Violet rays fall
on the dry Zinc plate electrons(the negatively charged particles)
are emitted from the Zinc plate.
ii) The neutral Zinc plate after emitting electrons (the negatively
charged particles), becomes positively charged .
iii)This phenomenon of emission of electrons is called Photoelectric
Effect.
iv)This phenomenon is used in the following devices :
1. Photoelectric cells
2. Recording and reproduction of sound in cinema films.
Ans.1 (j) (i)1. The material of fused
wire should have high resistance and low melting point such as tinoran
alloy of Tin and Copper.
2.The material of the heater element should have high resistivity and high
melting point such as Nichrome.
(ii) The angle of dip is defined as the angle made by the direction of
total resultant of magnetic field of the earth with the horizontal
direction in the magnetic meridian at that point
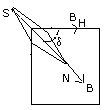
The angle d is the angle of dip .
1.The angle of dip d = 0 i.e minimum at the magnetic equator
2.The angle of dip d = 90o i.e the maximum at the
magnetic poles of earth.
|
|
Q 2(a) A block of mass 30 Kg is pulled
up a slope (Diagram 5 below) with a constant speed by applying a force of
200 N parallel to the slope. A and B are initial and final position of the
block.
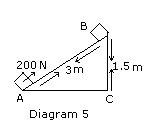
(i) Calculate the work done by the force in moving the block from A to B
(ii) Calculate the potential energy gained by the block.
Q 2 (b) Diagram 6 below gives an arrangement of single moving pulleys.
Copy the diagram
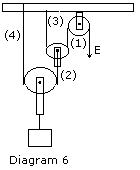
If the effort applied at the free end of the string is E,
(i) show the direction and magnitude of the forces exerted by the four
strings marked (1) to (4).
(ii) what is the load which can be lifted by the effort ?
(iii) calculate the mechanical advantage of the system of pulleys.
Q 2 (c) A block of wood is floating in water. The portion of the block
inside water measures 50 cm x 50 cm x 50 cm. What is the magnitude of the
buoyancy force acting on the block ?
|
|
Ans. 2:(a)(i)Let the
Work done in moving the block from A to B = W
Therefore W = F.S where F =200N and S= 3m
Hence, W =200 x 3 = 600 J
(ii)Potential energy gained by the block = mgh = 30 x 9.8 x
1.5 = 441 J
Ans. 2 (b)
(1)(ii) Suppose the load lifted = L
But effort applied = E (given)
Let the effort Arm = x
Then the load Arm = x/4
Now, by the principle of machine
Load X load Arm = Effort x Effort Arm
i.e L (x/4) = E(x)
Therefore , L = 4E
(iii) M.A is defined as the ratio of the load lifted by the
machine to
the effort applied on the machine
i.e M.A = L/E = 4E/ E = 4
Hence, M.A = 4 |
 |
Ans. 2 (c) The volume of the
displaced water = volume of immersed portion of the block of wood
= 50 x50 x50 cc =12500 cc
But, Mass of 1 cc of water = 1 gm
Therefore, mass of the displaced liquid = 12500 gm
But by law of floatation buoyant force = Weight of the displaced
water = 12500 X 980 dyne
or Force of buoyancy = (12500 x 980)/ 100000 N = 122.5 N
|
|
Q 3(a) A piece of metal at 10oC has a mass of 50g. When it is
immersed in a current of steam at 100oC,0.7g of steam is
condensed on it. Calculate the specific heat of of the metal.
Given : Latent heat of steam = 540 Cal/g.
Q 3 (b) Explain briefly :
(i) Why hot water bottles are very efficient for fomentation ?
(ii) How human body temperature is maintained at normal value (37oC)
when the atmospheric temperature rises as high as 45oC?
|
|
Ans. 3: (a) Let the
specific heat of given metal = C
By principle of calorimetry
Heat lost by steam = Heat gained by metal
m steam x L steam = m metal x
C x Rise in temperature
0.7 x 540 = 50 x C x (100 - 10)
Therefore , C = (0.7 x 540 )/ 4500 = 0.084 cal/g/oC
Ans. 3 (b)(i)Hot water bottles are very efficient for fomentation
because the specific heat of water is the largest of all other liquids, so
equal volume of water and of any other liquid, the water has largest
thermal capacity. Hence it will be very effective for fomentation.
(ii)The body maintains homeostasis in the body with reference to
temperature by the phenomenon of sweating . The excessive heat is
transferred by the blood to the skin surface, and water is evaporated
through sweat glands using the excess heat . Since water has a very high
latent heat of evaporation , a lot of heat is eliminated from the body
through this process i.e evaporation causes cooling.
|
|
Q 4(a) (i) State Snell's law of refraction of light.
(ii) Diagram 7 below shows a glass prism placed in minimum deviation
position. A ray of monochromatic light is incident on it's face AB.
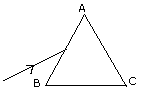
Copy the diagram and show the refracted ray and the emergent ray. Mark the
angle of deviation.
State any two factors on which the angle of deviation depends.
Q 4 (b) (i) Define dispersion of light.
(ii) Explain briefly how white light gets dispersed by a prism.
(iii) What is an impure spectrum?
|
|
Ans. 4:(a)(i)The
ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence in one medium at the point of
incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction in the other medium for a
given pair of two different media 'a' and 'b' is constant amb
which is known as the refractive index of medium 'b' with respect to
medium 'a''
i.e sin i/sin r =amb
(ii)

PQ is the incident ray of monochromatic light
QR is the refracted ray
 KTS = KTS = D
is the angle of deviation. D
is the angle of deviation.
We know that angle D = (m - 1) A
1.Therefore, D Á m i.e angle of deviation depends upon the
refractive index of the material of the prism
2.D Á A i.e the angle of deviation depends upon the angle of
the prism.
Ans. 4 (b) (i)Dispersion of light is the phenomenon of the
splitting up of the different constituent colors of the chromatic
light into its parts such as white light gets dispersed into seven colors
(VIBGYOR) on passing through a glass prism
(ii)

White light has seven colors viz. V I B G Y O R as shown in the
above diagram. These seven colors have different wavelengths hence deviate
through different angles on passing through the glass prism . Therefore
different colors are obtained separately as emergent rays falling on the
screen.
The red deviates least while the violet deviates the most.
(iii)An impure spectrum is that in which overlapping of two or more
different colors takes place.
|
|
Q 5(a) (i) State any two characteristics
of a wave motion.
(ii) What is the relation between frequency, wavelength and speed of a
wave?
(iii) A longitudinal wave of wavelength 1cm travels in air with a speed of
330m/s. Calculate the frequency of the wave.
Can this wave be heard by a normal human being?
Q 5 (b) Two waves A and B have
wavelengths 0.01 Ao and 9000 Ao respectively.
(i) Name the two waves.
(ii) Are the speeds of these two waves equal when they travel in vacuum ?
(iii) If the amplitude of a wave is doubled, what will be the effects on
its loudness?
|
|
Ans. 5:(a)(i)There
are various characteristics of wave motion out of which two are as under :
1. Wave motion is the form of physical disturbance which is produced in
the medium by repeated periodic motion of the particles of the medium
about their respective mean positions.
2. In the progressive wave motion the energy is transmitted along the wave
in its direction of propagation.
(ii) If n = frequency i.e the vibrations made by a particle/ sec.
l = wavelength of the given wave
v = speed of the wave
Then, v = n l
(iii) Wavelength l = 1 cm = 0.01 m (given)
Speed of the wave v = 330 m/s
But, v = n l
Therefore n = v/ l = 330 /0.01 = 33000 Hz which cannot be
heard as it is beyond the audible range 20 - 20000 Hz.
Ans. 5(b)(i) Wavelength of wave A = 0.01 Ao therefore it
is a g - ray
Wavelength of wave B = 9000 Ao so it is an infra-red ray.
(ii) Yes, both the waves are electromagnetic waves which travel in vacuum
with a speed of 3 x 108 m/s
(iii)We know that the loudness depends upon the intensity and the
intensity is directly proportional to the square of the amplitude
.Therefore on doubling the amplitude intensity will be four times higher.
Hence the loudness will increase four times.
|
|
Q 6(a) Given below is the circuit
diagram (Diagram 8) in which three resistances 1 ohm, 2 ohm, 3 ohm are
connected to a cell of e.m.f. 2 V and internal resistance 0.5 ohm.
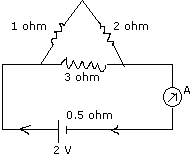
(i) Calculate the total resistance of the circuit.
(ii) What is the reading of the ammeter ?
(iii) What will be the ammeter reading if an exactly similar cell is
connected in series with the given cell ?
Q 6 (b) (i) Draw the neat labeled
diagram of an a.c. generator.
(ii) What is the magnitude of the e.m.f. induced in the coil when its
plane becomes parallel to the magnetic field ?
|
|
Ans. 6:(a)(i)

Let the total resistance of the circuit = R ohm
Resistance between P and N = RPN
But 1/RPN = 1/3 + 1/3 = 2/3 . Therefore RPN
= 3/2 = 1.5 ohm
Therefore R = RPN + 0.5 = 1.5 + 0.5 = 2 ohms
(ii)Let the reading of ammeter A = I1 ampere
Therefore E1=I1 R
Therefore I1 = E1/R = 2/2 = 1 ampere
(iii)

Let in this case the current in the circuit = I2
But the total e.m.f = E2 = 2V + 2V = 4V
Total resistance in the circuit =R2
Therefore R2 = RPN + 0.5 +
0.5 = 1.5 ohm + 0.5 ohm + 0.5 ohm = 2.5 ohm
Hence, I2 = E2/ R2 = 4V/2.5 ohms = 1.6
ampere
Ans. 6(b)

R1 and R2 = Slipring
B1 and B2 = Brass Brushes
R = Load Resistance
ABCD = Armature
(b)(ii)The magnitude of induced emf is maximum when the ratio of change of
flux is maximum. This happens when the plane of the coil lies parallel to
the magnetic field.
|
Q 7(a) (i) Draw a labeled
circuit diagram of a full-wave rectifier using two diodes.
(ii) Why is diode called a valve?
(iii) Draw two diagrams one above another, one showing the input and the
other showing the output in the above case.
Q 7 (b) (i) Draw a neat labeled diagram
of a modern X- ray tube.
(ii) What is the mechanism of energy production in a fission reaction?
|
Ans. 7:(a)(i)

In diagram P1 = plate of D1
P2 = plate of D2
P = primary coil of transformer
S = secondary coil of transformer
RL = load resistance
D1 and D2 are the two diodes
F1 and F1 is the filament of D1
F2 and F2 is the filament of D2
(ii) In a Diode , the electron are always
allowed to move from cathode to plate as plate is always at positive
potential with respect to cathode. A valve is a device which allows only
the unidirectional motion. So the Diode which allows unidirectional motion
of electron (i.e from cathode to plate) is called a valve.
(iii)

Ans. 7 (b)(i)Modern X-ray Tube OR Coolidge Tube

T = Tungsten Target
R = Copper rod
A.C = Anti-Cathode
L.T = Low Transition Battery
F = Filament
(ii) Nuclear fission is the phenomenon of
splitting of a heavy nucleus (usually A230) into two or more lighter
nuclei.
During the Fission-reaction certain mass disappears which is equal to the
difference of sum of masses of reactants and that of the products.
This difference in the masses is called mass defect ( m).
By Einstein's mass energy relationship the energy released during fission
is given by E = ( m).
By Einstein's mass energy relationship the energy released during fission
is given by E = ( m)c2
where, c = 3 x 108 m/s velocity of light in vacuum. m)c2
where, c = 3 x 108 m/s velocity of light in vacuum.
|






















