ICSE Set Qa1 Year Icse Economic98 Qa1.php Economics Exam Paper for students online
|
Q 4. (a) Differentiate between Sunk
Capital and Floating Capital. |
| Ans. (a)
Capital is the produced mean of production.
(I) Sunk capital is the capital which can produce only one commodity and can't be put to various uses. Such as :-In the ice factory, machines and buildings used to produce ice can't be used in production of anything else. So, these are sunk capital. (ii) Floating capital is the capital which can be put to alternative uses. such as :- money, fuel, etc. Ans. (b) Agriculture plays on important role in industrial development which can be explained as below :- (I) For industrial development, there is need to buy latest machinery etc. from foreign countries. For this foreign exchange is required which can be acquired through export of agricultural goods. (ii) More over some of the industries use agricultural products as inputs. such as : Textile industry is based on cotton, Sugar industry is based on sugar cane which are agricultural products. Ans. (c) Bank accounts are just like having money in hand as one can withdraw money whenever required and make use of it, More over bank interest is additional advantage to have money in bank account. Additional facilities, such as : Bank overdrafts etc. are to be provided only to the industrialists having bank account . So, it is better to have a bank account. Ans. (d) Jute industry is facing many problems in India. Some of them can be explained as below :- (I) Shortage and irregular supply of raw material : Raw material of jute industry is agricultural product which requires special environment to grow. It is being sown only in selective areas in India. But demand for jute is very high. Shortage of good quality of jute hampers the growth of jute industry. (ii) Competition : Jute industry is also facing a problem of world wide competition not only from other producers of jute but also from it's substitutes. Such as - Artificial fiber. |
|
SECTION - B Answer any four questions from this Section. |
| Q 5. (a) What is the meaning
of "land" in economic terms ? Discuss any four
peculiarities
of land as a factor of production.
(b) Discuss the importance of Small Scale Industries and Cottage Industries in the Indian economy. |
| Ans. (a)
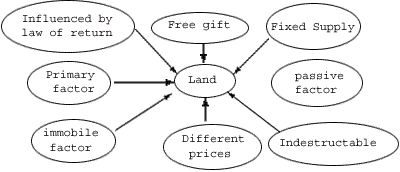
Land is the primary factor of production because land is needed for
starting any type of production.
Definition :- "By land means the material goods and the resources which 'nature' gives freely for man's aid, in land and water, in air and light and heat"- Marshall Peculiarities :- (I) Fixed supply : Total land supplied by nature can not be increased. The only way to increase its supply is to make intense use of land. (ii) Free gift of nature : Land is free gift of nature. Man has paid nothing to God for this. (iii) Indestructible factor : Land cannot be destroyed, but its shapes can be changed and its productivity can also change. (iv) Passive factor : Land is a passive factor of production because it cannot produce any thing by itself and man has to invest money and apply labour to get production from it.
Ans(b). Cottage and small scale industries play an important role in Indian economy which can be explained as below : (i) Equitable Distribution of Wealth : Growth of cottage and small scale industries has resulted in a rise in the income of many people by providing them employment .It leads to equitable distribution of wealth. (ii) Labor intensive : These industries are labor intensive industries and provide employment to a large number of people. (iii) Mobilization of savings: Idle savings of Indians can be utilized in these productive activities. These industries prove to be good means of mobilization of growing savings, talent and skill. (iv) Promote regional development :
These industries can be started in all parts of the country and these
play a major role in bringing about the proper regional development in the
country and the country needs it. |
| Q6 (a) Explain briefly the
meaning of efficiency of labor and state four factors which
determine
the efficiency of labor.
(b) What is meant by "agriculture labor" ? Give four reasons for the rapid growth of agricultural labor in India. |
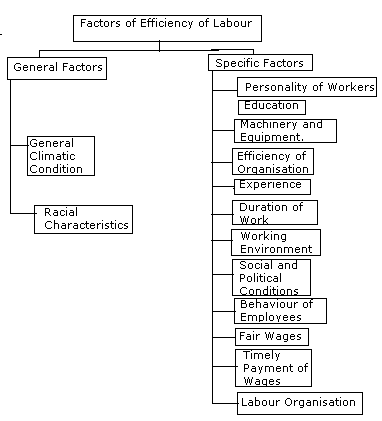
| Ans. (a) Efficiency
of labor is quality or ability of a worker to produce more and better
quality of goods in a specified time under some given conditions. Definition : "Efficiency of labor means the capacity of worker to produce."
Factors :
(1) Workers of cool temperature
regions are more efficient then the workers of tropical regions having hot
and moist climate. Similarly experience, favorable social and political situations, fair wages and timely payment of wages etc increases the efficiency of labor. Ans. (b) All those persons who derive a major part of their income as payment for work performed on the farms of others, can be designated as agricultural labour. Reasons for Rapid Growth of Agricultural labour :- (i) Capitalist Agriculture :- Pricing Policy of Govt., abolition of intermediaries, expansion of marketing have given rise to capitalist agriculture . A capitalist is in a position to compel the small holders of land to lower their prices which forced them to seek employment. (ii) Increased Population :- During the last decade, population in India has increased at a fast pace which has given rise to unemployment . The unemployed persons join as agricultural labour to earn their livelihood (3) Uneconomic Holdings :- The law of inheritance and decline of joint family system resulted in sub-division and fragmentation of holdings and uneconomical which forced small farmers to work on the farm. (4) Increase in Indebtedness :- There has been increase in indebtedness of small farmers. As they are unable to return the loan to money lenders, they are forced to work as tenants or work as agricultural labour. |
|
Q.7 (a) Describe the quantitative method of credit control adopted by the central bank to control credit. (b) What are the co-operative societies? Explain the three different ways in which is co-operative are organized in India. |
||||||||
| Ans. (a)
Policy of credit expansion and credit contraction is known as credit
creation. Policies of credit control are of two types quantitative and
qualitative.
Quantitative Techniques :- Quantitative techniques are method of controlling the total volume of credit with the help of bank rate , open market operation, change in cash reserve ratio and Liquidity Ratio . (1) Bank Rate :- Bank rate is the rate of interest at which the central bank rediscount the first class securities of other banks. Whenever central bank wants to expand credit it lowers the bank rate. (2) Open Market Operations:- Open Market operation refers to the sale and purchase of Government securities by the Central Bank in open market .When the central bank wants to contract the credit, it begins to sell the securities in the open market. When the central bank wants to expand credit, it begins to buy the securities in open market. (3) Cash Reserve Ratio:- Cash reserve ratio specifies the percentage of their total deposits, the commercial banks must keep with central bank . Higher the cash reserve ratio, lower will be the capacity of the commercial banks to create credit . When central banks wants to contract the credit , it increases the cash reserve ratio and when it wants to expand the credit, it decreases the cash reserve ratio. (4)Statutory Liquid Ratio:- This Ratio specifies the percentage of total deposits, commercial banks must keep in liquid form such as cash. Higher the Ratio, the lesser will be the capacity of commercial banks to create credit . When central banks wants to contract the credit , it increases statutory liquid ratio and when it wants to expand credit, it decreases the statutory Liquid Ratio. Ans (b) Co-operative societies are based on principle of self help through mutual help and gave moral and human touch to commercial activities . Definition:- " Co-operative organization is an association of weak who, gather together for a common economic need and try to lift themselves from weakness into strength through business organization." "Talmaki" Types of co-operatives Societies:- (1) Consumer's co-operative:- These societies are to be formed to supply consumer goods of standard quality to their members at fair prices. The consumers of a locality or town collect the necessary capital through share and start a consumer co-operative store. (2) Credit co-operatives:- These societies are formed to render the financial help to their members at reasonable rate of interest such as agricultural credit co-operative society etc. (3) Industrial Co-operative societies :- Producers jointly form industrial co-operative societies . They raise capital for society, elect the manager, undertake the risks, share profit and loss. (4) Co-operatives Housing societies:- These societies are formed to provide cheap houses to the members. |
||||||||
| Q8. (a) How is a Joint Stock
Company formed ? In what four respects does a Joint Stock Company differ
from a Partnership?
(b) Discuss two objectives of land reform and give a brief account of tenancy reforms in India. |
||||||||
| Ans: (a) "A
Joint Stock Company" is an artificial person created by law , having
a separate entity with a perpetual succession and a common seal."
Companies Act :-Steps in
formation of a joint stock company Private company can go for
commencement of business immediately after getting the certificate of
incorporation. But a public company has to undergo another two steps.
Ans (b) Land
reform measures are concerned with the abolition of intermediaries
under Zamindari system, improvement in the conditions of tenancy, ceiling
on holding of land and distribution of surplus land and consolidation of
the small and scattered pieces of land. (2) The old land system should be replaced by a new one . The land system should be free from exploitation. Tenancy Reform:- It was being realized that even the abolition of intermediaries does not necessarily mean abolition of tenants, because these intermediaries do not necessarily cultivate the land themselves . Realising the seriousness of tenancy problem, elaborate tenancy, legislation has been passed in almost all the states in recent years such as mentioned below. (1) Regulation of Rent :- Rent has been fixed at 1/6 of gross produce by the states of Rajasthan , Gujrat and Maharashtra , at 1/4 of G.P in Bihar , between 1/4 and 1/6 of gross product in Kerala etc. (2) Security of Tenure :- The legislation provided that tenants can't be ejected so long as they continue paying the rent. Maximum limit is fixed for self cultivation for land owners. (3) Conferment of ownership
rights to tenant:- Some states have given to the tenants the right to
purchase their holdings to encourage the cultivators to work hard. |
||||||||
| Q9 (a) What is meant by
subdivision and fragmentation of holdings ? Describe any four causes for
the subdivision and fragmentation of land holdings . (b) Examine any four reasons for the importance of good transport in a growing in economy like that of India . |
||||||||
| Ans (a)
The term sub-division and fragmentation means, The land holdings are
divided into small pieces of agriculture lands scattered at many
places" . It increases the cost of the management of agriculture and
makes the occupation of agriculture uneconomical . The following causes are responsible for the sub-divisional and fragmentation of land holdings :- (1) Law of Inheritance:-
According to Hindu code bill and Muslim personal law , The land of the
father is distributed among the children equally. The process goes
on resulting in sub-divisional and fragmentation of land holdings. (3) Decline of Joint family:- Every member wants to live separately with his family , so the land is divided into smaller pieces. This happens due to the downfall of the joint family system. (4) Rural Indebtedness:- Land is mortgaged to the money-lenders against loan borrowed . In absence of repayment of loan , the land is taken away by the money lenders . Ans.(b) The good transport system is important for the growing economies like India , due to the following four main reasons :- 1. Movement of raw material, fuels and machinery :-With the help of efficient and cheap transportation system, raw material, fuels and machinery etc. can be easily carried to the place of producing units, where these are needed. 2. Increase in the mobility of labour :- A good transport system helps in the mobility of labour . The underemployed and unemployed labour can get full employment. 3. Helps in national integration and human knowledge :- The good transport system helps in national integration and human knowledge because people can easily exchange their views by going from one place to another place. 4. More access to natural resources :- Development of the means of transportation will make it easy to have a access to the remote places having stock of natural resources. It will help the nation to grow at a faster pace. |
||||||||
| Q.10. (a) What is Economic
Planning ? Explain the reasons for the three Annual Plans
of
1966-'68, 1968-'69.
(b) Discuss any four functions of the Government in economic development. |
||||||||
Ans .(a) The
planning is the process by which pre-determined goals are achieved by
allocating the available resources within a specific period of time.
Therefore in planning the following three points are emphasized .
Definition :- "A scheme of economic organization in which individual and separate units, enterprises and industries are treated as coordinated units of one single system for the purpose of utilizing available resources to achieve the maximum satisfaction of the people's need within a given time." Prof Lewis Reasons for plan holiday:- The three annual plans were implemented after the failure of the 3rd five year plan from 1966-67, 1967-68 and 1968-69. The main reasons of this plan holidays are the following :- 1. Failure of IIIrd Five Year Plan :- The IIIrd five year plan failed badly to achieve its pre-determined targets . 2. Failure of monsoon in the year 1965-66 :- Due to poor monsoon, the production in agriculture sector fell down considerably which resulted in inflation in the economy. 3. Foreign exchange crisis :- The country faced the foreign exchange crisis and due to this , the devaluation of Indian rupee took place in the year 1966. Due to the above mentioned reasons, the govt .could not implement the fourth five year plan in time and instead of that it introduced three annual plans. Ans. (b) The four functions of the govt. in economic development are given below :- I Reduction in the Inequalities of Income and Wealth :- In most of the economies the distribution of income and wealth is unequal. It is not a desired goals from the point of view of the economies of welfare. It is true that the perfect equality of income and wealth is not possible . The welfare govt. in the modern economies always try to achieve the goal of equal distribution of income and wealth through the various measures like taxation on higher income, public distribution in favour of poors. etc. 2. Full employment :- The full employment is that situation in the economy when the involuntary unemployment is reduced to zero or to a minimum possible level. The govt. tries to provide employment to all the working population in the economy. For the achievement of this goal the govt. tries to increase the rate of capital formation which always results in production oriented employment in the economy. 3. Improvement in the standard of living :- The main objective of the economic development is welfare of the society. One of the criteria for measurement of the welfare and economic growth is the improvement in the standard of living of the people for this the real per capital income should go up in the society. 4. Social security :- People in developing countries have low income and feel insecure due to this reason. In case of unemployment ,sickness or accident, they feel much insecure. In case of the death of the earning hand in the family, family members feel more insecure. The reasons given above forced the govt to come forward . The govt should follow the method of social insurance schemes to improve social security in the country specially for lower income people. |
||||||||
| Q.11 (a) Discuss any
four reasons to show that rapid industrialisation of our country is
essential (b) What is fiscal policy ? How can fiscal policy be used for economic development . |
||||||||
| Ans. (a) Predominantly
Indian economy is an agricultural economy therefore the rapid
industrialization is must for the economy due to the following reasons:-
1. To Increase the National Income :- The industrialization can provide a continuous and secure basis for the rapid growth of income. Man by putting in more efforts can increase production and hence income. 2. To Increase the Employment Opportunity :- In India too much population depends on agriculture . The agriculture sector is marked by the seasonal and disguised unemployment . The rapid industrialization can provide the employment to the surplus labour from agriculture sector. 3. Increase the Capital Formation :- Due to increase in the industrialization, the employment will increase , which resulted in the increase in the income and saving . Increased saving will lead to increase in capital formation which will further lead to faster economic growth. 4. Balanced Economy :- The increased industrialization will reduce the dependence on agriculture. As a result there will be balanced growth of all the sectors in the economy. Ans. (B). The fiscal policy is the budgetary or taxation policy which influences the public expenditure and public revenue in the economy ,through taxation , public loan and means of financing, the deficit budget and minting of new currency notes. It is used as a weapon to stabilize the economy in the face of inflation or deflation. The fiscal policy can help economic development in the following way :- 1. It increases the aggregate savings in the economy by applying the cuts in the private and public consumption. Increase in saving increases capital formation. 2. It helps in directing the resources from less productive use to more productive uses and from socially less desirable uses to more desirable uses. 3. The fiscal policy helps the economies by safe-guarding it against inflation. 4. The fiscal policy eliminates the sectoral imbalances arising in the economy from time to time. 5. It helps in reducing the glaring economic inequalities by bringing about an equitable distribution of income and wealth.
|